Guide to the OWASP Top 10 for LLMs: Vulnerability mitigation with Elastic

New risks for modern applications
Industries, governments, and enterprises of all kinds have adopted large language models (LLMs) and generative AI (GenAI) into their operations and workflows, unlocking new possibilities for everything from customer interaction to complex data analysis. But with this innovation comes new challenges for security, observability, and data science teams. As organizations embed LLMs deeper into critical operations, they expose themselves to a new class of vulnerabilities that traditional security measures are often ill-equipped to handle.1 Recognizing this challenge, the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) has defined the definitive framework for navigating these risks in the OWASP Top 10 for LLM Applications.
Securing these complex AI ecosystems demands a unified platform approach that combines deep observability with powerful security analytics. The Search AI Platform is uniquely positioned to address modern threats. By providing a single, integrated solution for security, observability, and data management, Elastic enables organizations to protect the entire LLM application stack. Elastic provides coverage from the prompts and responses to the underlying infrastructure, APIs, data, and downstream systems that the models interact with.2 This blog provides a guide on using Elastic's capabilities to mitigate each vulnerability in the OWASP Top 10 for LLMs.
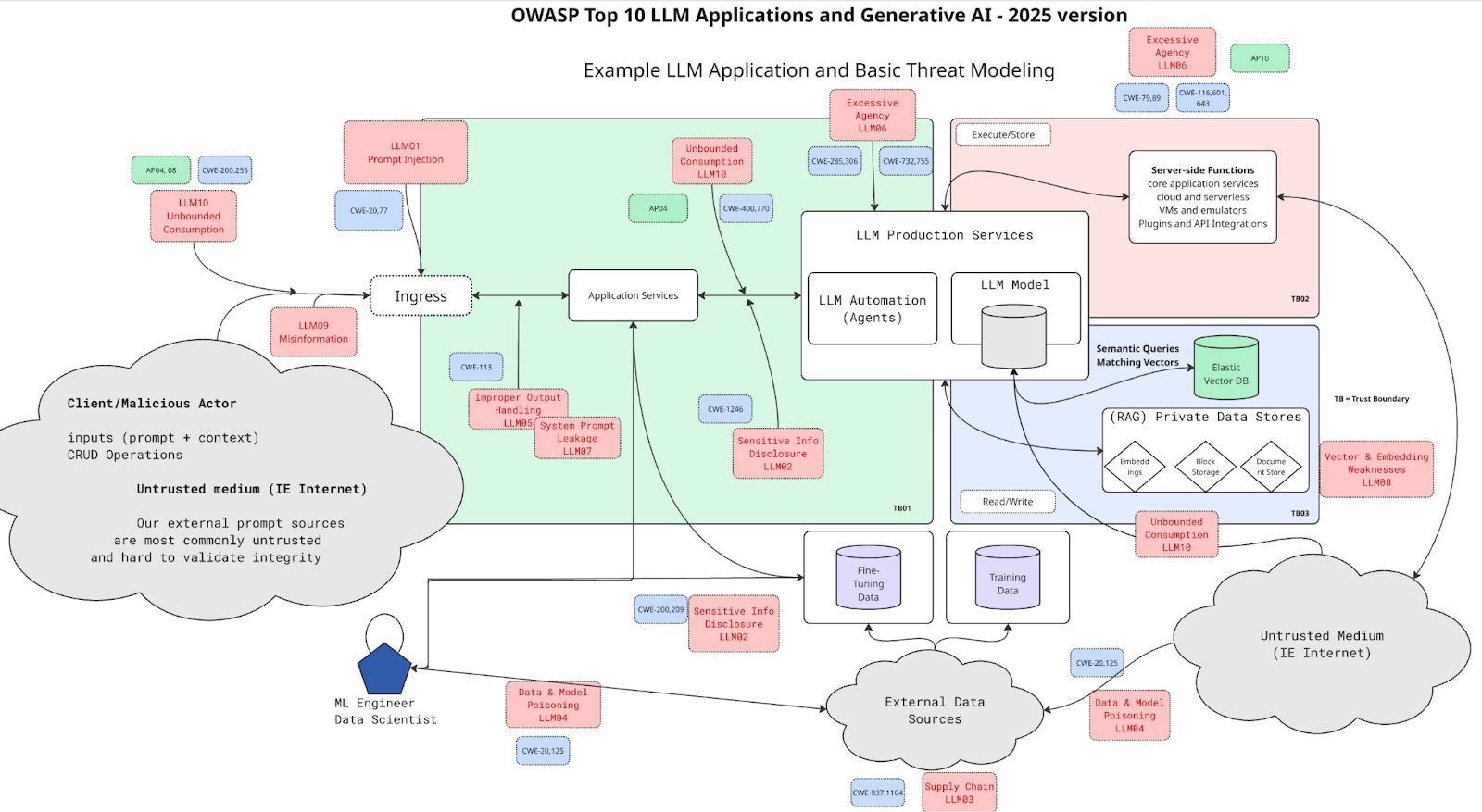
A unified architecture
Securing a modern GenAI application isn’t a matter of addressing a single layer. It requires an in-depth strategy that provides visibility and control points at every stage of an LLM-powered transaction. Elastic provides the unified foundation for such an architecture, correlating signals from the user's prompt all the way to the backend infrastructure — a feature only available via a combination of data management, observability, and security along with software engineering best practices.
This architecture demonstrates how Elastic serves as the central nervous system for GenAI security:
Input and application layer: User prompts and external data enter the LLM application. Elastic application performance monitoring (APM) instruments this layer, providing transaction tracing and the opportunity for proactive data filtering to mitigate sensitive data disclosure (LLM02).
LLM and retrieval augmented generation (RAG) layer: The application interacts with the LLM and Elasticsearch as a vector database. Logs and metrics from the LLM provider are ingested, enabling detection of unbounded consumption (LLM10). Within Elasticsearch, native features like document level security (DLS) enforce permission-aware RAG, mitigating vector and embedding weaknesses (LLM08).
Downstream systems: The LLM agent may interact with backend APIs, databases, or other servers. These systems are monitored by Elastic Defend and APM, which detect the effects of attacks like improper output handling (LLM05) or excessive agency (LLM06).
The Elastic Search AI Lake: All of this telemetry consisting of logs, metrics, traces, and security events is ingested and normalized into a single Elasticsearch data store.
Analytics and action layer: Atop this unified data, Elastic Security and Elastic Observability work in conjunction. The detection engine — powered by Event Query Language (EQL) and machine learning (ML) — correlates events across layers to find complex attacks like prompt injection leading to remote code execution (RCE) (LLM01). Observability dashboards and alerts provide the tools to monitor misinformation (LLM09), supply chain vulnerabilities (LLM03), and model poisoning (LLM04). It also provides proactive warnings for financial and resource consumption risks.
Mapping the OWASP LLM Top 10 to Elastic solutions
To provide a clear roadmap, the following table summarizes how the Elastic platform's core pillars and capabilities map directly to the mitigation strategies for each OWASP LLM vulnerability. This summary demonstrates the comprehensive nature of the Elastic solution.
| OWASP LLM vulnerability | Primary Elastic solution pillars | Key Elastic capabilities | Mitigation strategy summary |
| LLM01: Prompt Injection | Elastic Security, Elastic Observability | Detection engine (EQL), machine learning, APM, gen_ai ECS fields | Detect anomalous downstream behavior resulting from malicious prompts and correlate with suspicious inputs for high-fidelity alerts. |
| LLM02: Sensitive Information Disclosure | Elastic Security, Elastic Observability | APM data filters, ingest pipelines, natural language processing (NLP), prebuilt detection rules | Proactively sanitize data in transit and at rest; discover and classify sensitive data; detect the misuse of any leaked credentials. |
| LLM03: Supply Chain Vulnerabilities | Elastic Security | Vulnerability management (CNVM), file integrity monitoring (FIM), CI/CD log analysis | Centralize vulnerability data from scanners; analyze software bill of materials (SBOMs); monitor model and data files for integrity; and detect anomalies in the machine learning operations (MLOps) pipeline. |
| LLM04: Data and Model Poisoning | Elastic Security, Elastic Observability | Machine learning, FIM, role-based access control (RBAC) | Detect behavioral anomalies in model outputs and performance indicative of poisoning; and protect RAG knowledge bases from unauthorized modification. |
| LLM05: Improper Output Handling | Elastic Security, Elastic Observability | APM distributed tracing, prebuilt detection rules | Trace malicious LLM outputs to downstream systems and detect the resulting exploit, such asSQLi, RCE, at the point of impact. |
| LLM06: Excessive Agency | Elastic Security, Elastic Observability | Machine learning, APM, lateral movement detection | Monitor all agent actions (API calls and processes); baseline normal behavior with ML; and detect anomalous activity indicative of compromise or hallucination. |
| LLM07: System Prompt Leakage | Elastic Security | Machine learning, prebuilt detection rules | Mitigate the impact of a leak by detecting the anomalous use of exposed credentials or configurations, making the prompt's content irrelevant. |
| LLM08: Vector and Embedding Weaknesses | Elasticsearch, Elastic Security | DLS, RBAC, machine learning | Enforce permission-aware RAG with native DLS; and monitor for anomalous query patterns that could indicate data poisoning or inversion attacks. |
| LLM09: Misinformation | Elasticsearch, Elastic Observability | Vector search, hybrid search, machine learning, alerting | Power reliable RAG systems with advanced retrieval; and monitor RAG quality metrics and enable human-in-the-loop feedback workflows. |
| LLM10: Unbounded Consumption | Elastic Security, Elastic Observability | Machine learning, LLM integrations, Kibana Alerting | Monitor real-time token usage and cost metrics; use ML to detect anomalous consumption spikes; and configure budget-based alerts for Denial of Wallet (DoW) prevention. |
Learn more
Confidently building, deploying, and scaling the next generation of AI-powered applications requires Search AI Lake, observability, and security platforms that are as integrated, intelligent, and adaptable as the AI systems that they are designed to protect. The Search AI Platform provides this comprehensive, in-depth foundation that enables organizations to innovate with AI while effectively managing the full spectrum of risks outlined in the OWASP Top 10 for LLMs. To learn more, read the full white paper.
Sources
- OWSAP, “OWASP Top 10 for LLM Applications 2025,” https://genai.owasp.org/resource/owasp-top-10-for-llm-applications-2025, 2024.
The release and timing of any features or functionality described in this post remain at Elastic's sole discretion. Any features or functionality not currently available may not be delivered on time or at all.
In this blog post, we may have used or referred to third party generative AI tools, which are owned and operated by their respective owners. Elastic does not have any control over the third party tools and we have no responsibility or liability for their content, operation or use, nor for any loss or damage that may arise from your use of such tools. Please exercise caution when using AI tools with personal, sensitive or confidential information. Any data you submit may be used for AI training or other purposes. There is no guarantee that information you provide will be kept secure or confidential. You should familiarize yourself with the privacy practices and terms of use of any generative AI tools prior to use.
Elastic, Elasticsearch, and associated marks are trademarks, logos or registered trademarks of Elasticsearch N.V. in the United States and other countries. All other company and product names are trademarks, logos or registered trademarks of their respective owners.