Elastic Inference Service for self-managed clusters
Elastic Inference Service (EIS) is available with zero setup on Elastic Cloud Hosted and Serverless deployments. To use EIS with other deployment types, you can use Cloud Connect. Cloud Connect enables you to use Elastic Cloud services in your self-managed cluster without having to install and maintain their infrastructure yourself.
You can use EIS to enable features such as:
For a full list of EIS-powered features, refer to AI features powered by EIS.
Before you can use EIS with your self-managed cluster, ensure you meet the following requirements:
- Your self-managed cluster is on an Enterprise self-managed license or an active self-managed trial license
- You have an Elastic Cloud account with either an active Cloud Trial or billing information configured
-
Open Cloud Connect
In your self-managed Kibana instance, navigate to the Cloud Connect page using the search bar.
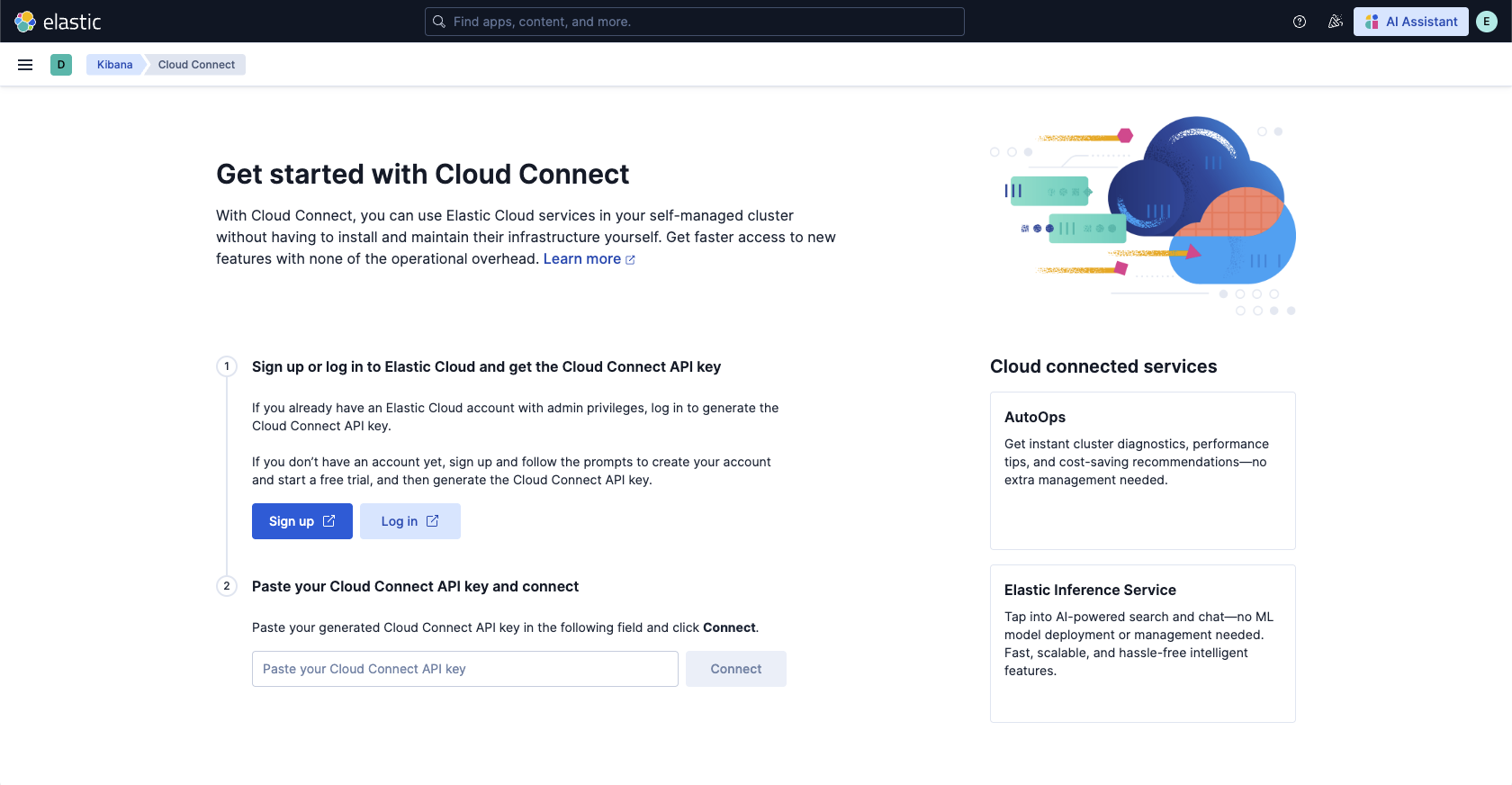
-
Get your Cloud Connect API key
Sign up or log in to Elastic Cloud and get the Cloud Connect API key:
- If you don’t have an account yet, click Sign up and follow the prompts to create your account and start a free Cloud Trial.
- If you already have an Elastic Cloud account, click Log in.
-
Connect your cluster
Copy the Cloud Connect API key, paste it into your self-managed cluster's Cloud Connect page, then click Connect.
-
Enable Elastic Inference Service
On the Cloud connected services page, click Connect for Elastic Inference Service.
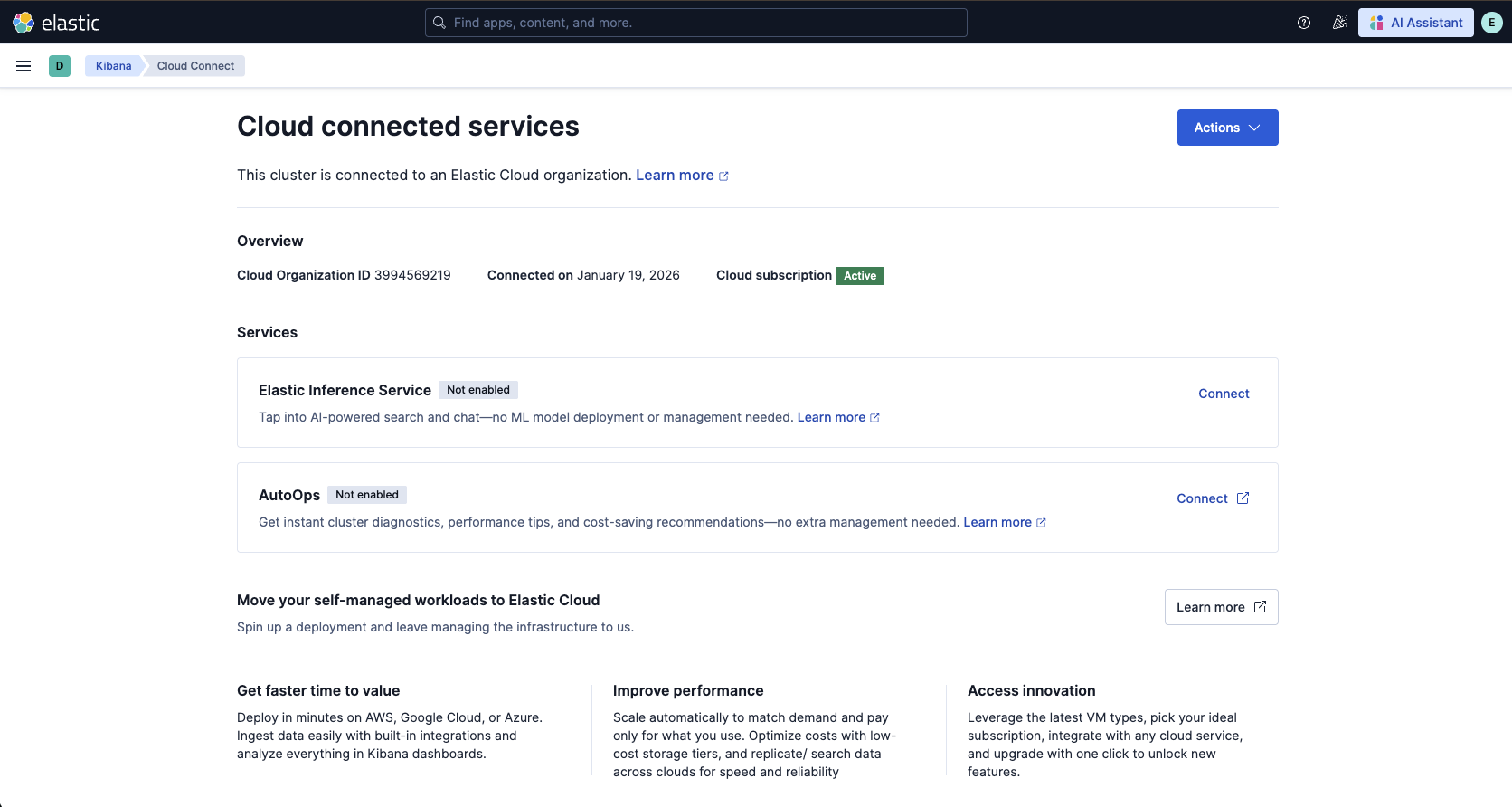
After you connect Elastic Inference Service through Cloud Connect, Elasticsearch automatically creates multiple inference endpoints for search and chat use cases, along with corresponding Kibana AI connectors. Supported Kibana features now use these connectors automatically.
In this example, you create an index with a semantic_text field, index a document, then run a query that returns a semantically related match.
In Dev Tools, run the following requests:
-
Create an index with a
semantic_textfieldPUT /semantic-search-eis{ "mappings": { "properties": { "text": { "type": "semantic_text" } } } }- Because you already enabled EIS, the
semantic_textfield type uses EIS through the default inference endpoint (.elser-2-elastic). To learn more, refer tosemantic_text.
- Because you already enabled EIS, the
-
Index a document
POST /semantic-search-eis/_doc{ "text": "Aberdeen Football Club" } -
Run a search query
GET /semantic-search-eis/_search{ "query": { "match": { "text": "soccer" } } }
The response should include the indexed document:
{
"took": 161,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 4.729913,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "semantic-search-eis",
"_id": "oyH935sBG2FaZ-zOMrer",
"_score": 4.729913,
"_source": {
"text": "Aberdeen Football Club"
}
}
]
}
}
Using Elastic Inference Service through Cloud Connect, you have access to all available models listed under Supported models, including LLMs, embedding models, and rerankers.
To use these models, you need Kibana connectors (for LLMs) or inference endpoints. There are preconfigured inference endpoints for all models. For some LLMs, connectors need to be created manually, depending on the model.
For Claude 3.7 and Claude 4.5, connectors are preconfigured and ready to be used.
To use other LLMs listed under Supported models, you must create the Kibana connectors manually. The corresponding inference endpoints are preconfigured.
Predefined inference endpoints and connectors are available for all models listed under Embedding models and Rerankers.
For these models, you only need to create new inference endpoints if you want to use custom settings.
For information about EIS regions and request routing, refer to Region and hosting.
EIS is billed per million tokens and consumes ECUs. For details on pricing and usage tracking, refer to Pricing and Monitor your token usage.